India's Multi-Fuel Journey Towards Sustainable Mobility and Energy Independence
India's automotive sector is driving a major shift with a multi-fuel approach—balancing affordability, innovation, and sustainability to reduce emissions, enhance energy security, and support its net-zero and energy independence goals.
For decades, the automotive industry has been at the forefront of criticism for its significant contribution to environmental challenges, including air pollution, extensive land use for roads, parking facilities, and massive energy consumption. These issues are particularly acute in urban areas.
It is estimated that road transportation, encompassing cars, two-wheelers, trucks, and buses, accounts for approximately 25% of global CO₂ emissions. While there is a pronounced focus on minimizing the carbon footprint in vehicle production and usage, there remain numerous avenues through which the industry can further mitigate its environmental impact.
According to the Ipsos Global Trends Report of 2024, a striking 82% of Indian citizens believe that we are heading for environmental disaster unless we change our habits quickly.
Public sentiment indicates a shared responsibility among governments, businesses, and consumers to combat climate change. The transition to sustainability is driven not only by public and governmental pressure but also by investor expectations. As the automotive industry strives to reduce mobility-related carbon footprints, the journey towards a low-carbon future is contingent on several factors—chief among them affordability, infrastructure readiness, and energy security.
With the rising demand for cost-effective transportation and a commitment to reducing carbon emissions, a multi-fuel strategy is poised to play a pivotal role in steering India towards a sustainable future.
India's quest for energy independence is encapsulated in its multi-fuel strategy, which encompasses electric vehicles (EVs), biofuels, hydrogen fuel cells, and natural gas. This comprehensive approach is designed to diminish reliance on imported crude oil, mitigate pollution, and address climate change.
The automotive industry is not unanimously settled on a singular sustainability strategy. While some original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are fully committed to electrification, others see promise in hybrids, hydrogen fuel cells, or technological enhancements to traditional combustion engines, suggesting they may outperform battery electric vehicles (BEVs) in environmental friendliness particularly in the commercial vehicle sector, there is competition among diesel, CNG, liquefied natural gas (LNG), hydrogen internal combustion engines, hydrogen fuel cells, and electric vehicles.
India stands uniquely positioned amidst this transition. The nation's automotive industry is undergoing a paradigm shift, exploring a wide range of alternative, less energy-intensive options. Investments span across technologies from CNG to biogas, hybrids to hydrogen, and electric vehicles, driving a comprehensive shift in mobility.
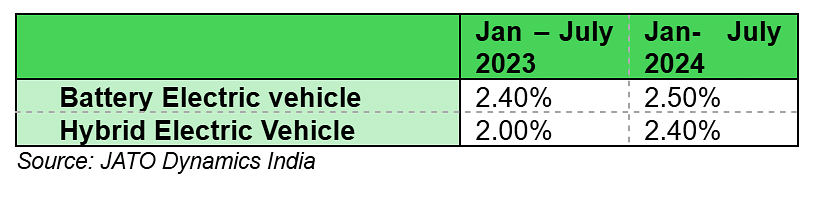
In the passenger vehicle segment, despite the robust push for electrics, EVs currently share the market space with hybrids. Government advocacy primarily targets EV adoption as a long-term objective, while hybrids are considered a pragmatic intermediary, potentially expediting the uptake of electric powertrains. However, tax structures pose significant challenges, dampening EVs' appeal among consumers.
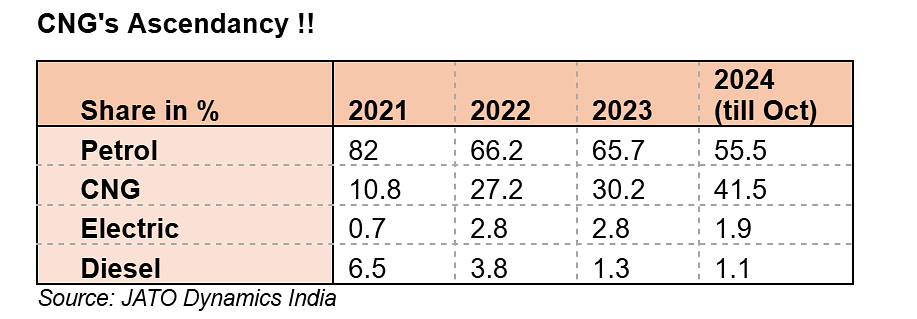
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) has emerged as a frontrunner, especially gaining momentum in the small commercial vehicle and three-wheeler sectors. Within a landscape where affordability is paramount, CNG is lauded for cost efficiency without compromising driving experience. For owners of three-wheelers and small commercial vehicles, CNG represents a substantial advantage for business operations and livelihoods, offering superior cost-efficiency ratios for long-distance and frequent drivers.
Ethanol blending also garners substantial attention from Indian OEMs. Having achieved a 12% ethanol blend in petrol by 2023, the target is set at 20% by the end of 2025. Other emerging fuel options include compressed biogas (CBG), a renewable natural gas derived from organic waste, and growing interest in green hydrogen, generated through renewable electricity. These innovations are crucial in realizing India's energy independence goals by 2047 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
Finally, the Indian automotive industry stands at a critical juncture of transformation, transitioning from a primary source of CO₂ emissions to champions of sustainable practices. A heightened environmental consciousness among the populace forms a foundation for a collective endeavour involving government and businesses to tackle climate change.
The industry's multifaceted fuel strategy, encompassing hybrids, CNG, hydrogen, ethanol, biogas, and electric vehicles, is tailored to meet diverse consumer demands. Economic considerations, particularly affordability, bolster CNG’s prominence, especially in the commercial arena.
Government incentives stimulate innovation and investments in clean technologies despite existing policy challenges. Looking ahead, India's automotive sector is poised for significant growth, projected to become the world's third largest by 2030, hinging on advancements in infrastructure and alternative fuels to secure energy independence by 2047 and accomplish net-zero emissions by 2070.
Prasad Joshi is Associate Director, Market Strategy & Understanding (MSU) at Ipsos India & Sanket Paranjpe is Research Manager, Market Strategy & Understanding (MSU) at Ipsos India. Views expressed are the author's own.
RELATED ARTICLES
EV Financing as a High-Growth Lending Segment for Green NBFC’s
India's electric mobility shift is no longer aspirational—it's a USD 200 billion capital opportunity where green lending...
EV Financing as a High-Growth Lending Segment for Green NBFC’s
India's electric mobility shift is no longer aspirational—it's a USD 200 billion capital opportunity where green lending...
EV Financing as a High-Growth Lending Segment for Green NBFC’s
India's electric mobility shift is no longer aspirational—it's a USD 200 billion capital opportunity where green lending...






 02 Jun 2025
02 Jun 2025
 3533 Views
3533 Views





 Autocar Professional Bureau
Autocar Professional Bureau


