Full Analysis of India-UK Free Trade Agreement
For the UK, this represents its most significant bilateral trade achievement since Brexit, while for India, it marks the first major FTA with a developed Western economy.
The India-United Kingdom Free Trade Agreement (FTA), signed on July 24, 2025, represents an important moment in bilateral economic relations between the world's fifth and sixth-largest economies. The agreement, formally known as the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA), aims to double bilateral trade from the current $60 billion to over $100 billion by 2030, while addressing complex issues ranging from automotive tariffs to professional mobility.
Context and Significance
The Indo-UK FTA arrives at a critical juncture in global trade, marked by rising protectionism and the reorganization of global supply chains. For the UK, this represents its most significant bilateral trade achievement since Brexit, while for India, it marks the first major FTA with a developed Western economy. The agreement's 27 chapters encompass goods, services, digital trade, intellectual property, and labor mobility, reflecting the complexity of modern trade relationships.
The negotiations, which began in January 2022, weathered political transitions in both countries before reaching conclusion in May 2025. The formal signing during Prime Minister Modi's visit to London symbolizes not just economic cooperation but also strategic alignment in the Indo-Pacific region.
Major Provisions: A Detailed Analysis
1. Tariff Elimination and Reduction Framework
Overall Structure
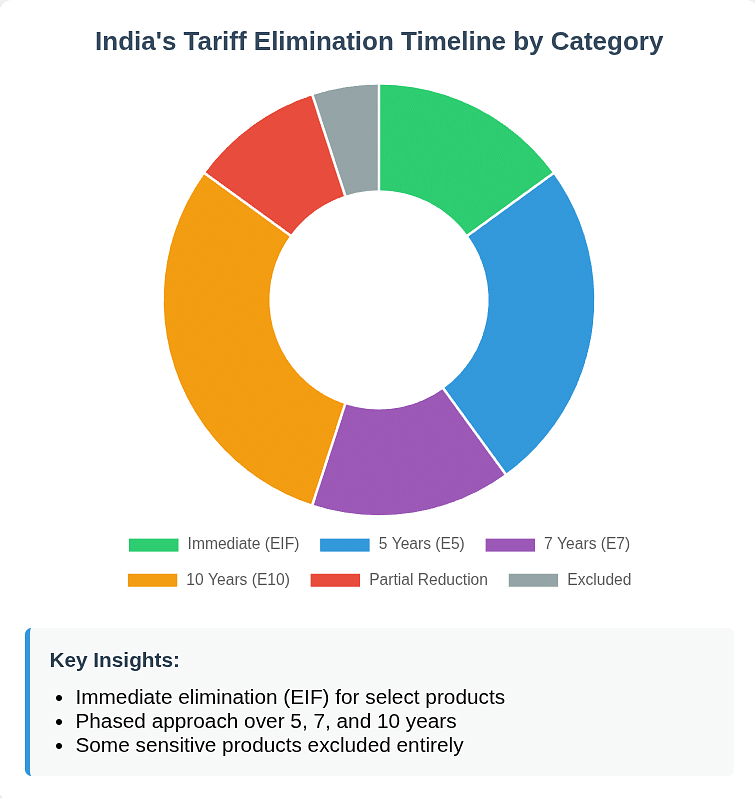
The FTA establishes a comprehensive tariff elimination schedule that fundamentally reshapes market access between the two nations. According to the official document, India commits to eliminating or reducing tariffs across multiple staging categories:
- Immediate Elimination (EIF): Customs duties on goods in this category are eliminated upon the agreement's entry into force
- Phased Elimination: Various categories (E5, E7, E10) provide for gradual elimination over 5, 7, or 10 years
- Partial Reductions: Categories like 'R5 to 50%' reduce tariffs to specified percentages of base rates
The UK's commitment is even more extensive, with 99% of Indian tariff lines receiving duty-free access, covering almost 100% of trade value by volume.
Implementation Timeline
The agreement adopts a calendar-year approach, with the first year running from the date of entry into force until December 31, and subsequent years following the calendar. This structured approach ensures predictability for businesses planning long-term investments and trade strategies.
2. Automotive Sector: Quotas and Transformative Changes
The automotive provisions represent perhaps the most contentious and transformative aspects of the FTA. The document reveals a complex Tariff Rate Quota (TRQ) system with significant implications:
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
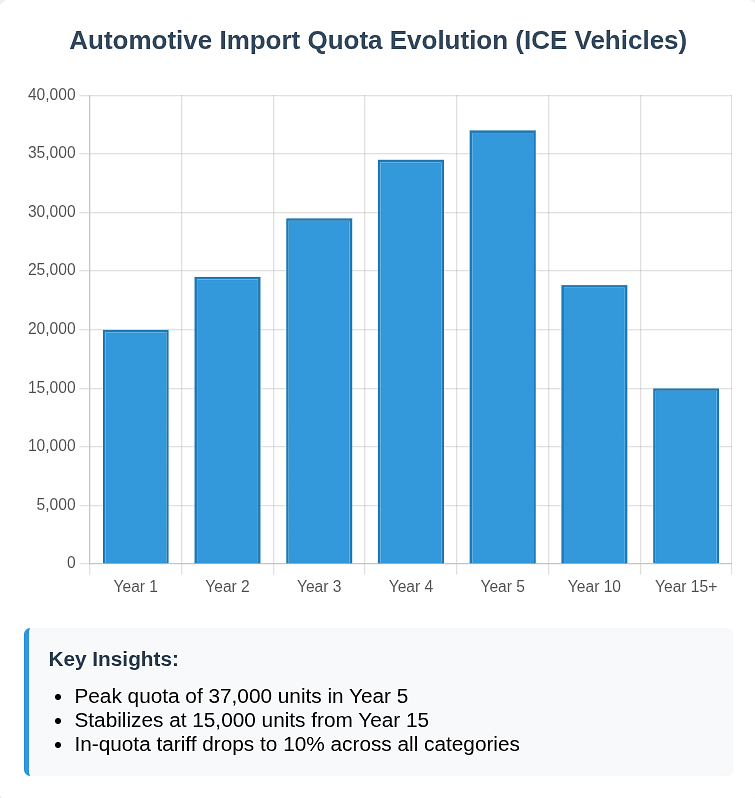 The TRQ for ICE passenger cars shows a nuanced approach:
The TRQ for ICE passenger cars shows a nuanced approach:
- Year 1: 20,000 total units with in-quota tariffs ranging from 30% (for vehicles over 3000cc) to 50% (for smaller engines)
- Progressive Expansion: Quota increases to 37,000 units by Year 5, then gradually decreases to 15,000 units from Year 15 onwards
- Tariff Reduction: In-quota tariffs eventually stabilize at 10% across all categories
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
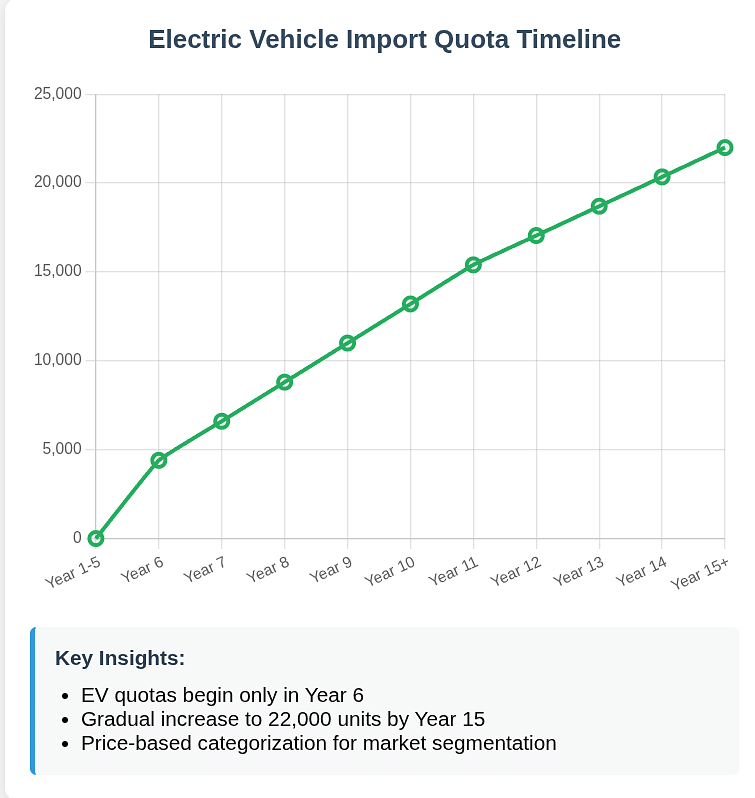
The EV quota structure reveals India's cautious approach to protecting its nascent electric vehicle industry:
- Delayed Start: EV quotas begin only in Year 6 with 4,400 units
- Price-Based Categories: Differentiation between vehicles below £40,000, £40,000-£80,000, and above £80,000
- Growth Trajectory: Quota expands to 22,000 units by Year 15
Impact Analysis
The automotive provisions will likely create a two-speed market in India. Premium British brands like Jaguar Land Rover, Bentley, and Rolls-Royce will benefit from significant tariff reductions, making luxury vehicles more accessible to India's growing affluent class. However, the quota system protects domestic manufacturers from being overwhelmed by imports, allowing time for the Indian automotive industry to enhance competitiveness.
The exclusion of zero-emission two-wheelers, buses, and trucks from tariff concessions demonstrates India's strategic approach to protecting sectors crucial for mass mobility and commercial transport.
3. Alcoholic Beverages: The Whisky Revolution
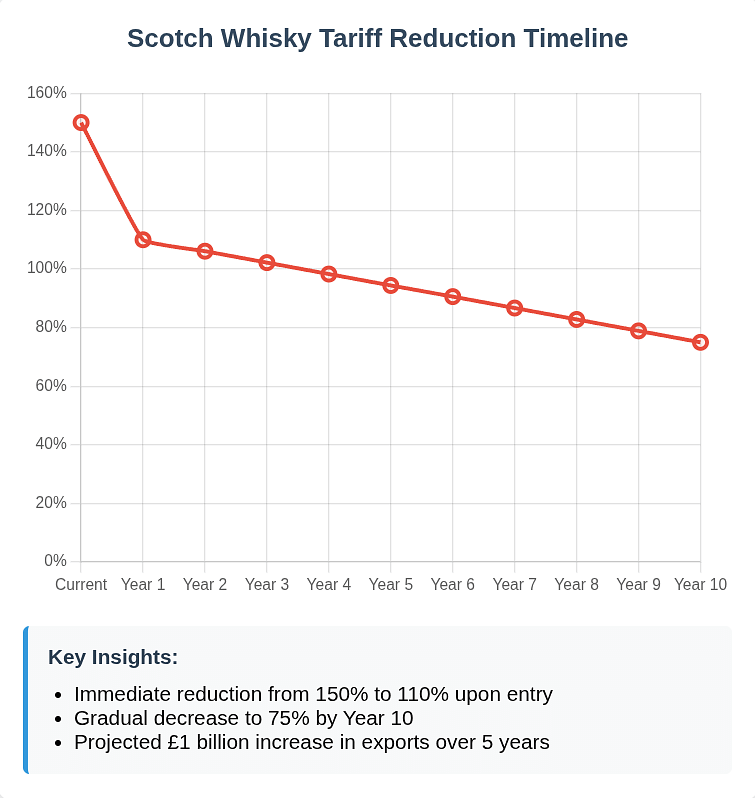
The treatment of alcoholic beverages, particularly Scotch whisky, has garnered significant attention:
Tariff Structure
- Immediate Reduction: From 150% to 110% upon entry into force
- Gradual Decline: Reaching 75% by Year 10
- Minimum Import Price: USD 5 per liter or USD 6 per 750ml bottle
- Inflation Indexation: MIP values indexed every 15 years based on India's Wholesale Price Index
Market Implications
The Scotch Whisky Association's projection of £1 billion in additional exports over five years appears realistic given the tariff trajectory. However, the Minimum Import Price mechanism ensures that only premium products benefit, protecting India's mass-market domestic spirits industry. This clever design allows India to capture revenues from luxury consumption while safeguarding employment in local distilleries.
4. Textiles and Apparel: Unleashing Export Potential
The immediate duty-free access for 99% of Indian textile exports to the UK represents a game-changer for India's labor-intensive textile sector:
Competitive Advantage
- Elimination of 2-18% tariffs places Indian textiles on par with competitors like Bangladesh
- Covers the entire value chain from yarn to finished garments
- Includes technical textiles, an area where India has developing expertise
Employment Impact
Industry estimates suggest the textile provisions could create 500,000-1,000,000 jobs in India over the next decade, particularly benefiting women workers who constitute a majority in this sector. The agreement's emphasis on labor-intensive sectors aligns with India's demographic dividend strategy.
5. Professional Services and Labor Mobility
The services provisions, particularly those relating to professional mobility, represent innovative approaches to modern trade:
Key Features
- Mode 4 Access: Facilitation of temporary movement of professionals
- Social Security Agreement: Three-year exemption from UK National Insurance contributions for Indian professionals
- Mutual Recognition: Framework for professional qualifications recognition
Strategic Significance
These provisions acknowledge the reality of global talent flows and India's competitive advantage in services. The social security exemption alone could save Indian IT companies and their employees millions of pounds annually, enhancing the competitiveness of Indian service providers.
6. Digital Trade and E-commerce
While specific digital trade provisions aren't detailed in the excerpted document, news reports indicate comprehensive coverage of:
- Data flows and localization
- Electronic authentication
- Consumer protection in digital markets
- Intellectual property in the digital sphere
These provisions position both countries to benefit from the digital economy's expansion while maintaining regulatory sovereignty.
7. Pharmaceutical and Healthcare
The pharmaceutical sector provisions balance innovation incentives with access to medicines:
Market Access
- Reduced tariffs on medical devices from the UK
- Streamlined regulatory procedures for pharmaceutical products
- Protection for generic medicines through careful intellectual property provisions
Public Health Safeguards
The agreement appears to maintain India's ability to produce generic medicines, crucial for global public health, while providing enhanced IP protection for innovative drugs.
8. Financial Services
The financial services chapter opens new opportunities:
- Enhanced market access for UK insurers and asset managers
- Facilitation of fintech collaboration
- Regulatory cooperation mechanisms
This could accelerate India's financial sector modernization while providing UK firms access to one of the world's fastest-growing financial markets.
Economic Impact Assessment
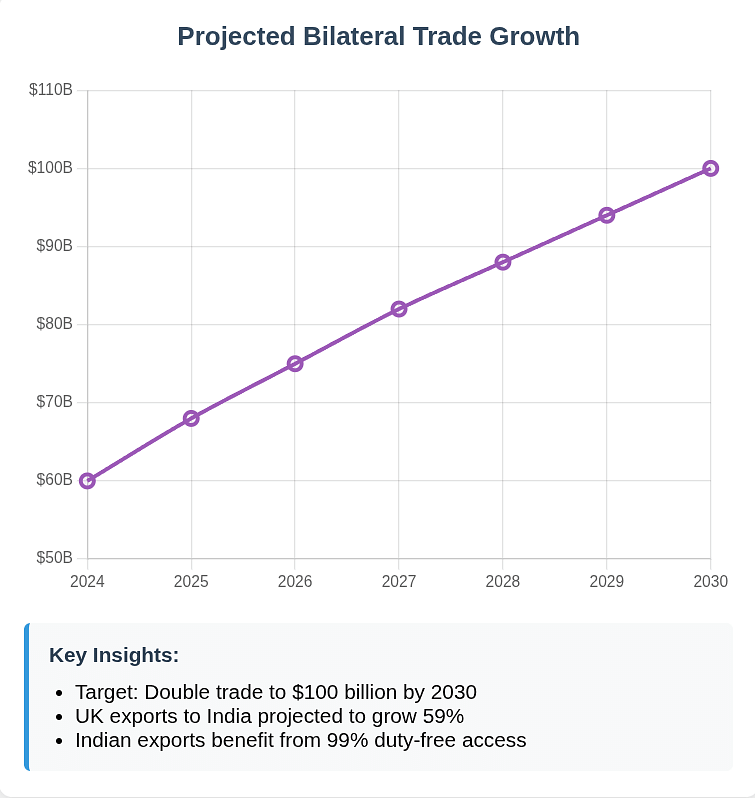
Macroeconomic Projections
Based on government assessments and independent analysis:
GDP Impact
- UK: £4.8 billion annual increase by 2040 (0.1% of GDP)
- India: Proportional gains expected, though specific figures vary
Trade Expansion
- Bilateral Trade Target: $100 billion by 2030 (from current $60 billion)
- UK Exports to India: Projected increase of £15.7 billion by 2040 (59% growth)
- Indian Exports to UK: Expected to grow proportionally
Sectoral Winners
In India:
- Textiles and Apparel: 30-40% export growth projected
- IT and Professional Services: Enhanced competitiveness through social security benefits
- Pharmaceuticals: Improved access to UK's regulated market
- Engineering Goods: Tariff elimination on 99% of products
In the UK:
- Scotch Whisky: £1 billion additional exports over 5 years
- Luxury Automobiles: Access to India's growing premium market
- Financial Services: Entry into high-growth Indian market
- Medical Devices: Reduced tariffs improving competitiveness
Employment Effects
The agreement's focus on labor-intensive sectors suggests significant job creation potential:
- Direct Employment: 1-2 million jobs across textiles, services, and manufacturing
- Indirect Employment: Supply chain effects could double direct impact
- Skill Development: Pressure to upgrade skills in competitive sectors
Consumer Benefits
Indian consumers stand to gain from:
- More affordable luxury goods (cars, whisky, electronics)
- Greater product variety and quality
- Competitive pressure improving domestic products
UK consumers benefit from:
- Cheaper textiles and apparel
- Diverse food products
- Competitive services, particularly in IT
Implementation Challenges and Risk Factors
1. Utilization Rates
Historical FTA utilization in India averages only 25%, compared to 70-80% in developed countries. Key barriers include:
- Complex rules of origin requirements
- Lack of awareness among SMEs
- Documentation and compliance costs
2. Trade Balance Concerns
India's past FTA experience shows imports growing faster than exports. The UK FTA includes several mechanisms to prevent this:
- Phased liberalization allowing adjustment time
- Sectoral carve-outs protecting sensitive industries
- Regular review mechanisms
3. Domestic Industry Adjustment
Certain sectors face adjustment pressures:
- Automotive Components: Competition from UK suppliers
- Spirits Industry: Premium segment competition from Scotch
- Dairy and Agriculture: Though protected, political sensitivities remain
4. Regulatory Harmonization
Despite the agreement, non-tariff barriers could limit benefits:
- Standards and certification differences
- Regulatory approval timelines
- Professional qualification recognition delays
5. Geopolitical Factors
External factors could impact implementation:
- Global trade tensions
- Carbon border adjustments
- Supply chain reorganization
Strategic Implications
For India
The FTA represents several strategic achievements:
- Diversification: Reduces dependence on traditional partners
- Value Chain Integration: Facilitates movement up the value chain
- Services Champion: Reinforces India's services export leadership
- Investment Gateway: Positions India as a manufacturing hub for UK companies targeting Asia
For the UK
The agreement delivers on multiple strategic objectives:
- Post-Brexit Validation: Demonstrates ability to negotiate significant trade deals
- Indo-Pacific Tilt: Concrete manifestation of strategic pivot
- Services Access: Opens one of the world's largest services markets
- Supply Chain Diversification: Reduces dependence on other major economies
Bilateral Relationship
Beyond economics, the FTA strengthens the strategic partnership:
- Enhanced technology collaboration
- Defense industrial cooperation
- Climate change partnership
- Educational exchanges
Recommendations for Stakeholders
For Businesses
-
Immediate Actions:
- Analyze tariff schedules for products
- Review supply chain optimization opportunities
- Assess market entry strategies
-
Medium-term Planning:
- Invest in compliance infrastructure
- Develop partnerships across markets
- Plan workforce skill upgrades
-
Long-term Strategy:
- Consider investment opportunities
- Build brand presence in new markets
- Integrate into bilateral value chains
For Policymakers
-
Implementation Support:
- Develop comprehensive awareness programs
- Simplify documentation requirements
- Create dedicated FTA utilization cells
-
Domestic Industry Support:
- Provide adjustment assistance
- Facilitate technology upgrades
- Support export readiness programs
-
Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Track utilization rates
- Monitor trade balance
- Regular stakeholder consultations
For Workers and Professionals
-
Skill Development:
- Upgrade technical skills
- Develop cross-cultural competencies
- Understand new market requirements
-
Mobility Preparation:
- Understand visa provisions
- Prepare for international assignments
- Build professional networks
Future Outlook
The Indo-UK FTA sets precedents for India's future trade negotiations:
Template for Future Agreements
The balanced approach to goods, services, and investment provides a model for negotiations with the EU and others.
Evolution of Provisions
Regular review mechanisms allow for:
- Expansion of quotas
- Deepening of commitments
- Addition of new sectors
Regional Integration
The FTA could catalyze:
- UK-India-third country value chains
- Regional services integration
- Technology cooperation triangles
Conclusion
The Indo-UK Free Trade Agreement represents a carefully balanced outcome that advances both nations' economic interests while protecting sensitive sectors. Its innovative provisions on services, digital trade, and professional mobility reflect 21st-century trade realities. While implementation challenges exist, the agreement's comprehensive nature and built-in flexibility mechanisms provide a robust framework for expanding bilateral economic engagement.
Success will depend on effective implementation, high utilization rates, and continuous adaptation to changing global conditions. For businesses, the agreement opens significant opportunities but requires strategic planning to maximize benefits. For policymakers, supporting implementation while managing adjustment costs remains crucial.
As both nations navigate an uncertain global environment, this FTA provides a stable foundation for economic partnership. Its true success will be measured not just in trade statistics but in jobs created, innovations fostered, and the strategic partnership strengthened. The agreement stands as testament to what patient negotiation can achieve and offers hope for continued global economic integration despite rising protectionist pressures.
The Indo-UK FTA is more than a trade deal—it's a strategic bet on the future of the bilateral relationship and a blueprint for modern, comprehensive economic partnerships. As implementation begins, all stakeholders must work together to ensure this historic agreement delivers on its tremendous promise.
RELATED ARTICLES
Electric Bike Sales Soften in July as China Restrictions Take Hold
After remaining largely unaffected in May and June thanks to pipeline inventory, sales of electric 2-wheelers have start...
Little Impact of China's Rare Earth Blockage in June e2Wheeler Sales
India’s electric two-wheeler market continued to go from strength to strength in June 2025, even notching up a 32% yoy j...
India's Electric Car Market Sets New Record in June
Sales reached a record 13,178 units, up from 12,304 units in May and 12,233 in April, spurred by new models such as Cret...





 By Arunima Pal
By Arunima Pal
 24 Jul 2025
24 Jul 2025
 1218 Views
1218 Views





 Autocar Professional Bureau
Autocar Professional Bureau




