Can India’s auto industry live up to the AMP export target?
Automobile and auto component manufacturers need to aggressively target new global markets if they are to achieve export-led growth.
The Automotive Mission Plan (AMP) of 2016 set by the government of India had set an ambitious target of generating US$145 billion in total output for the automobile and auto-component industry by 2016 through concentrated efforts on export of small cars, MUVs, two-wheelers, three-wheelers and auto components.
However, due to the economic slowdown experienced by the sector between 2011 and 2014, the establishment failed to achieve certain targets and implement the requisite policies. The ‘Make In India’ week held in February 2016 in Mumbai led to the introduction of many new policies and MoUs being signed between the government and the auto industry.
Exports can tap under-utilised capacity
The Indian automotive market at 24 million units is currently the seventh largest in the world in terms of total production of automobiles with an annual YoY increase of 7.22% between FY2014 and FY2015. It is poised to be the third largest car manufacturer by FY 2020. The annual turnover is also slated to increase from US$74 billion in FY2015 to a massive US$ 300 billion by FY2020.
However, as reported earlier by Autocar Professional, the growth led by the auto and auto component industry still suffers from certain grey areas like under-utilisation of capacity which leads to increase in overhead costs or over utilisation of capacity leading to dependence on exports. However, exports cannot be a life-saver at all times.
Stiff targets in AMP 2026
The Automotive Mission Plan (AMP) of 2026 is aimed at not only achieving the targets which were not met during the previous plan but also generate new ones with regards to mobility, safety, pollution, employment generation, scaling the exports to 35-40% of its overall output and having a comprehensive and stable policy dispensation to nurture the automobile industry. It further states that the government and the automobile industry will work together to strengthen the industry by achieving an annual output target of Rs 16,16,000 crore to Rs 18,89,500 crore by 2026. It also aims to make India the largest manufacturer/ seller of small cars, two-wheelers, three-wheelers, tractors and buses in the world as well as the third largest with regard to passenger vehicle and heavy trucks, all amounting to a contribution greater than 12% of the national GDP from the current 7.1%.
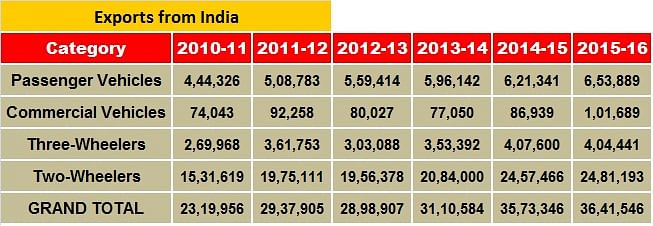
In FY2015, total automobile exports at 3.64 million units registered an annual increase of 1.91% as compared to 3.57 million units in FY14. This pales in comparison to the increase in exports of almost 15% between FY2013 and FY2014 which shows major volatility in the export trend for the Indian automotive industry.
The seminar on ‘Making India a Global Manufacturing Hub for Auto and Auto Components’ held February 17, 2016 during the Make In India Week discussed the need for auto and component manufacturers to make competitively in India in order to emerge as a major export hub of the world. Frugal engineering in auto production such as the Renault Kwid and investments in R&D testing facilities will prove to be a catalyst in achieving this target.
The Indian auto component industry is currently estimated to be around US$40 billion with exports valued at US$11 billion and the SME sector contributing to almost 80% towards manufacturing of the auto components. This is slated to increase to US$115 billion by FY2020. This has been a result of extensive investments by both the national and global manufacturers in R&D, electronics, safety, global sourcing, and innovation.
Over the five-year period of 2010-15, total automotive exports grew at a CAGR of 9.37% which is impressive given the slack in automotive demand and production. Passenger vehicle exports grew at 8.02%, commercial vehicles at 6.42%, three-wheelers at 8.47% and two-wheelers at 10.14% over the same period.
Automotive exports are expected to grow at a CAGR of 3% between FY2015 and FY2026 which amounts to more than 5 million units.
A helping hand
In order to achieve this, the government plans to further improve exports to major global markets by the implementation of the ‘Merchandise Exports from India Scheme’. Under this scheme, the export markets are divided into 3 categories:
Category A: Traditional Markets (30), European Union (28), USA, Canada.
Category B: Emerging and Focus Markets (139), Africa (55), Latin America and Mexico (45), CIS countries (12), Turkey and West Asian countries (13), ASEAN countries (10), Japan, South Korea, China, Taiwan.
Category C: Other markets (70).
The various points covered in this scheme would be trade facilitation, ease of doing business, incentive programs, transparency and digitisation of procedures. Also area-based incentives have been proposed for setting up SEZs in areas like Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand to encourage further developments with regards to automotive production and exports.
Additionally, the government plans to introduce the export promotion capital goods scheme, duty remission scheme and product focus schemes to further increase the export of automobile components. This would be mainly aimed at engine and engine parts, transmission and steering parts, suspension and braking parts, equipment and metal parts.
Recommended:
- AMP 2006-2016 falls short of some targets but vrooms overall
- Honda beats Hero, becomes largest scooter exporter for FY2015-16
RELATED ARTICLES
TVS Motor: The New King of India's Electric 2-Wheeler Market
January 2026 sees TVS Motor solidify its position with 34,558 units Bajaj struggles to keep pace.
Electric PV Sales Stabilize after GST Hit
Fresh FADA data shows January 2026 registrations surging 55% year-on-year, with Tata, JSW MG, and Mahindra all posting s...
Bajaj Chetak production plunges by 47% in July due to shortage of rare earth magnets
Bajaj Auto manufactured 10,824 Chetaks last month, 9,560 fewer units than the 20,384 Chetaks produced in July 2024. As a...






 13 May 2016
13 May 2016
 21889 Views
21889 Views





 Angitha Suresh
Angitha Suresh


 Arunima Pal
Arunima Pal

 Ajit Dalvi
Ajit Dalvi

