Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill, 2019 passed in Rajya Sabha
The government asserts that the amendments in the Motor Vehicles Bill will improve road safety, facilitate citizens in their dealings with transport departments, strengthen rural transport, public transport and last mile connectivity through automation, computerisation and online services.
The much-awaited Motor Vehicles Amendment Bill, 2019 was passed by the Rajya Sabha on July 31, 2019. Being debated for almost three years, the new bill focuses on improving road safety, facilitate citizens in their dealings with transport departments, strengthen rural transport, public transport and last-mile connectivity through automation, computerisation and online services.
Nitin Gadkari, Minister of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) asserted that states that the new Bill would, in no way, encroach upon their powers and authorities, but rather empower the states, and will provide an efficient, safe and corruption-free transport system in the country. As the bill has been passed with three amendments, it will need to go back to Lok Sabha. The Lok Sabha had already passed the Bill on July 23, 2019.
The new bill incorporates recommendations of the Group of Transport Ministers (GoM) of States constituted by the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways to address the issue of road safety and to improve the facilitation of the citizens while dealing with transport departments. The GoM was headed by Yoonus Khan, former Transport Minister of Rajasthan, and had 18 State Transport Ministers from different political parties as members.
Important highlights
The earlier bill, which was drafted over three decades ago, had many shortcomings especially in terms of keeping up with the evolution of the Indian automotive industry, technologies and infrastructure among others. As a result, in addition to updating earlier clauses, the new Bill has introduced a number of new rules.
Some of the important areas where the bill has focused on include —
- Improving road safety by increasing penalties to act as a deterrent against traffic violations. Stricter provisions in respect of offences like juvenile driving, drunken driving, driving without a licence, dangerous driving, over-speeding, overloading and others. Stricter provisions for helmets have been introduced along with provisions for electronic detection of violations. Penalty regarding motor vehicles is to be increased by 10 percent every year.
- The bill mandates automated fitness testing for vehicles to reduce corruption in the transport department while improving the roadworthiness of the vehicle. Failing to meet the same will attract a penalty for deliberate violation of safety/environmental regulations, this is also extended to bodybuilders and spare part suppliers. The testing agencies issuing automobile approvals have been brought under the ambit of the Act and standards will be set for motor vehicle testing institutes. Interestingly, the Bill also calls for a compulsory recall of defective vehicles and power to examine irregularities of vehicle companies.
- In case of a recall, the central government can order a recall of motor vehicles if a defect in the vehicle may cause damage to the environment, or the driver, or other road users. The manufacturer of the recalled vehicle will be required to: reimburse the buyers for the full cost of the vehicle, or replace the defective vehicle with another vehicle with similar or better specifications.
National Road Safety Board
The Bill will see the central government a National Road Safety Board to advise the central and state governments on all aspects of road safety and traffic management including standards of motor vehicles, registration and licensing of vehicles, standards for road safety, and promotion of new vehicle technology.
In terms of addressing road fatalities and promote people to come forward to help road accident victims, for which the Good Samaritan guidelines have been incorporated in the Bill. It defines a Good Samaritan as a person who renders emergency medical or non-medical assistance to a victim at the scene of an accident, and provides rules to prevent harassment of such a person.
Furthermore, the Bill provides for a scheme for cashless treatment of road accident victims during the 'Golden Hour', which refers to the immediate one-hour time period following a traumatic injury, during which, chances of preventing death by way of prompt medical treatment are the highest.
What may come as a boon to commercial vehicle users, the Bill makes a provision for driver’s attendant to be included in Third Party insurance. There will be no cap on liability of insurers. There will be a 10 time increase in insurance compensation, from Rs 50, 000 to Rs 500,000. Insurance firms will have to pay claims within a month, if the victim’s family agree to accept Rs 500,000 compensation. The Bill also increases the minimum compensation for hit and run cases from Rs 25,000 to Rs 200,000 in case of death, and from Rs 12,500 to Rs 50,000 in case of grievous injury.
Setting up a accident fund
The Motor Vehicle Amendment Bill will see the central government start a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund, which will provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in India. The fund will be utilised for: treatment of persons injured in road accidents as per the golden hour scheme, compensation to representatives of victims who lose their lives in a hit and run accident, person grievously hurt in a hit and run accident, and compensation to any other persons as prescribed by the central government. This Fund will be credited through: payment of a nature notified by the central government, a grant or loan made by the central government, balance of the Solatium Fund (existing fund under the Act to provide compensation for hit and run accidents),or any other source as prescribed the central government.
E-governance and regulating cab aggregators
One of the key aspects that the Bill focuses is on using digitalisation to improve delivery of services to the stakeholders, this includes - provision for online driving licenses, vehicle registration, driver training. The government is also looking to develop an integrated 'Transport System', which will be possible from the 'National Transportation Policy'. This will also enhance the powers of the state governments, provide better last-mile connectivity, rural transport and similar others.
While India has seen the rise of shared mobility, through various fleet aggregators operating in the country, there has been no policy to regulate their functioning. To address this, the Bill has defined aggregators as digital intermediaries or market places which can be used by passengers to connect with a driver for transportation purposes (taxi services). The Bill provides guidelines for aggregators.
Interestingly, the Bill has also asked for fitness check of vehicles to be computerised and to bring out a vehicle scrappage policy.
The bill has been amended on the basis of recommendations of the Group of Transport Ministers and other pressing requirements, the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways introduced the Motor Vehicle (Amendment) Bill 2016.
Fines for traffic offences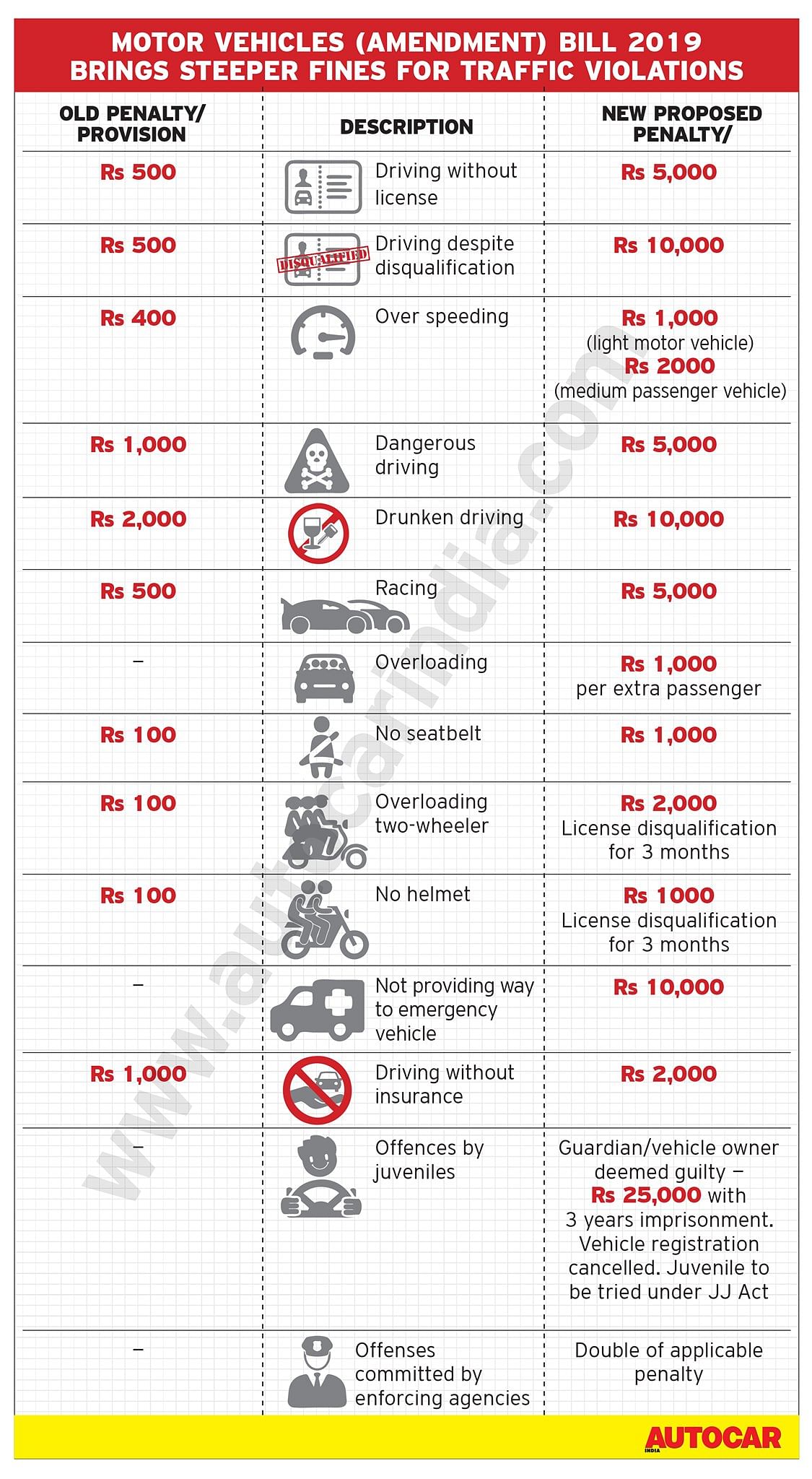
RELATED ARTICLES
Cosmo First diversifies into paint protection film and ceramic coatings
The Aurangabad, Maharashtra-based packaging materials supplier is leveraging its competencies in plastic films and speci...
JSW MG Motor India confident of selling 1,000 M9 electric MPVs in first year
The 5.2-metre-long, seven-seater luxury electric MPV, which will be locally assembled at the Halol plant in Gujarat, wil...
Modern Automotives targets 25% CAGR in forged components by FY2031, diversifies into e-3Ws
The Tier-1 component supplier of forged components such as connecting rods, crankshafts, tie-rods, and fork bridges to l...






 By Autocar Professional Bureau
By Autocar Professional Bureau
 01 Aug 2019
01 Aug 2019
 9364 Views
9364 Views









