Mazda, Saudi Aramco and AIST to collaborate for reducing CO2 emissions
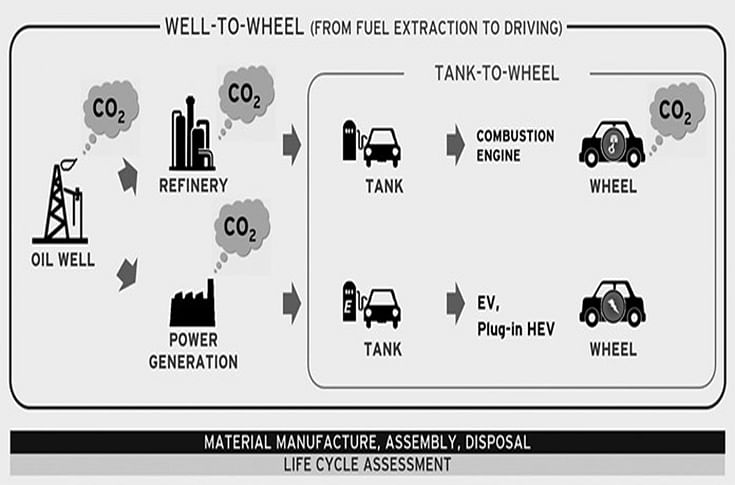
Their aim is to develop advanced engine/fuel combinations with improvements in engine efficiency and CO2 reductions assessed from a well to wheel basis.
Mazda Motor corporation has announced the start of a joint research project with Saudi Aramco, the state-owned oil company of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) to make internal combustion engines (ICE) more efficient and for reducing carbon dioxide emissions as assessed from a well to wheel basis. The research topic focuses on developing a low-carbon fuel along with research into internal combustion engines that use the fuel.
Within this project, Saudi Aramco will develop a fuel based on a refinery process that results in lower carbon dioxide emissions. Mazda and AIST will research and develop a high-efficiency engine that will run on this fuel. Mazda’s contribution will be a high-efficiency advanced prototype engine based on their SKYACTIV technologies. The entire scope of research will be tested and optimised at AIST headquarters in Tokyo. The program consists of a thorough CO2 assessment through refinery modelling, engine testing, spray diagnostics, and computational fluid dynamics simulations. The anticipated benefit of this approach is a holistic view of the ICE’s environmental impact.
Saudi Aramco supports Gasoline Compression Ignition (GCI) technology as a viable development route to achieving high fuel efficiency with low emissions and new fuel formulations to further complement this engine concept. The GCI concept, which is Saudi Aramco’s flagship project within this research program, is expected to enable 25-30 percent reduction in CO2 as compared to conventional gasoline spark-ignition engines. Mazda’s advanced prototype engine is based on a compression ignition engine with ultra-lean burn combustion.
The GCI fuel has a lower carbon content and higher heating value than commercial diesel and gasoline fuels. The lean burn engine emits lower CO2 than conventional gasoline engines. The companies expect that the combination of the engine and fuel technologies will deliver substantial savings in well-to-wheel CO2 emissions.
Mazda, AIST and Saudi Aramco believe that this new collaboration will showcase the ICE platform’s abundant potential for cost-effective efficiency improvement and reduced GHG emissions. The joint work is expected to be completed in fiscal 2020.
Also read: Mazda's new IC engine that rivals EVs
Maharashtra to get a mega refinery from Saudi Aramco and Indian Consortium
RELATED ARTICLES
Autoliv Plans JV for Advanced Safety Electronics With China’s HSAE
The new joint venture, which is to be located strategically near Shanghai and close to several existing Autoliv sites in...
JLR to Restart Production Over a Month After September Hacking
Manufacturing operations at the Tata Group-owned British luxury car and SUV manufacturer were shut down following a cybe...
BYD UK Sales Jump 880% in September to 11,271 units
Sales record sets the UK apart as the largest international market for BYD outside of China for the first time. The Seal...






 By Autocar Professional Bureau
By Autocar Professional Bureau
 08 Aug 2018
08 Aug 2018
 5306 Views
5306 Views





 Ajit Dalvi
Ajit Dalvi




