Innovation in vehicular testing
New system developed by Yaamini and Bharathi proposed that test data could be wirelessly transmitted between vehicle and diagnostic station.
These components have to be tested in all kinds of terrains and climates which can take a physical toll on the testing engineers. Testing engineers Yaamini and Bharathi, who often had to brave inclement weather and odd work hours, then came upon the idea of harmonising automotive electronics testing with telemetry. Their idea was first described in a research paper presented at the SAE 2006 Commercial Vehicle Engineering Congress & Exhibition held in Rosemont, IL, USA in October 2006.
The research paper described the cost effectiveness of using telemetry in advanced testing methodology. It said that as the use of electronics in commercial vehicles in India and other developing countries was still at a nascent stage there were tremendous cost benefits to be derived from using telemetry in keeping testing costs down even while ensuring that each component was tested to its limits in all climatic conditions.
HOW IT ALL WORKS
The conventional testing methodology followed during any electronic unit or embedded system employs data acquisition devices for capturing data in real time. This allows test and development engineers to select desired sampling frequency and rectify system faults quickly. Though this system has advantages, it also imposes limitations on the number of parameters that can be captured.
More importantly, this system requires that a trained technician or engineer be present on site to operate the data-capture devices and monitor the process. The other drawbacks relate to mounting the data-capture device, and the possibility that the devices could get damaged due to heat or during torture track testing.
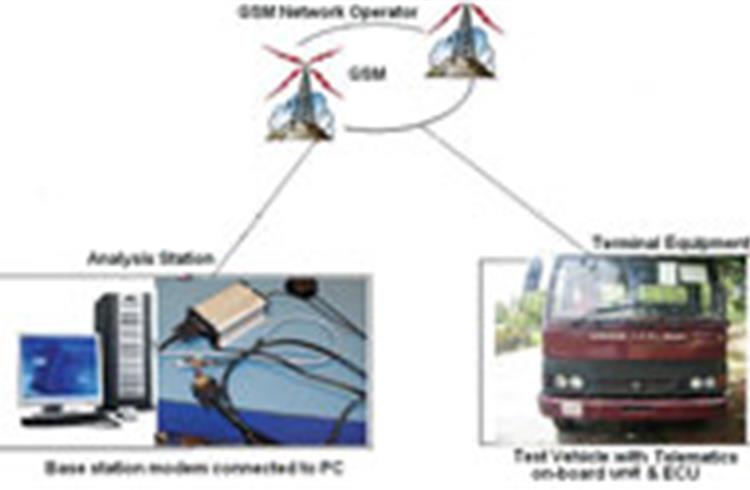
The new system devised by Yaamini and Bharathi proposed that test data could be wirelessly transmitted between the vehicle and the diagnostic station. The automotive applications of telemetry are presently confined to vehicle tracking and remote diagnostics and maintenance to an extent. The methodology developed by the duo employs telemetry for the testing of an electronic control unit.
##### They used GSM technology, which besides voice communication is also capable of data communication, as the basis for their new data-capture system. Data communication manifests itself as the short messaging system (SMS) in cellphones and comes as a basic feature with all SIM cards. In this mode, data transmission as point-to-point communication takes place in packets with a block length of 140 bytes.
To enable data transmission, test system components such as electronic control unit, base station modem, on-board unit with antenna and RS232 to RJ11 converter are deployed. In this system, the electronic control unit is mounted on the test vehicle and it is connected to the on-board unit. RS232 communication protocol is used between the on-board unit and the electronic control unit. GSM is used for the wireless transmission of the data from the test vehicle to the analysis station.
In the analysis station, the base station modem is installed. Simple UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) communication is used for capturing the data in the computer. UART is a standard peripheral that enables serial communication on any embedded device. UART is commonly used with RS232 for embedded systems to communicate between microcontrollers and PCs. The young duo used it to communicate between base station modem and the computer, by making necessary communication port and mode settings.
SEVERAL BENEFITS
Yaamini and Bharathi say that this testing methodology has several benefits including remote monitoring of data on real time basis and the possibility of standardising test and data capture processes. This could eventually lead to easier testing when more complex electronic or embedded systems become part of commercial vehicles in India.
They point out that their system requires lesser manpower and saves time besides supporting simultaneous testing and data analysis using low cost equipment. This concept can be extended to two-way data communication for interrogating and programming the electronics of motor vehicles in future, they add.
Dr Arvind Bharadwaj, head of advance engineering division of Ashok Leyland said that harmonising automotive electronics testing using telemetry was a breakthrough concept. “The data captured during their testing experience was found to reduce test cycle time significantly. I view this as a very important first step for our company towards realising an innovation culture,” he said.
RELATED ARTICLES
BRANDED CONTENT: Eliminating the worries of battery charging with smart solutions
The charging infrastructure is the backbone of electric mobility but is also one of the key perceived barriers to EV ado...
The battery-powered disruptor
Greenfuel Energy Solutions is planning to shake up the EV battery market with the launch of a portfolio of specially eng...
SPR Engenious drives diversification at Shriram Pistons & Rings
The engine component maker is now expanding its business with the manufacturing of motors and controllers through its wh...





 By Autocar Pro News Desk
By Autocar Pro News Desk
 04 May 2007
04 May 2007
 2237 Views
2237 Views